Swap Rates in Trading: What Are They and What’s Their Impact on Your P&L
Swap rates play a crucial role in CFD and forex trading, often representing the most significant cost that traders must pay. This cost, paid or received to hold an open position overnight, is a key factor every trader must know about, learn how to calculate, and assess for its impact on their P&L (Profit & Loss).
On this page, we provide a brief explanation of what swap fees are in trading and how they can impact your profitability. Let’s get to it.
What Are Swap Rates in Forex and CFD Trading?
In forex and CFD trading, swap rates are the overnight financing charges or credits applied to long and short positions held beyond the trading day's close. In simpler terms, they are the interest paid or received on a trade carried into the next day. These fixed-rate debt rates exist because when you trade on margin, you are effectively borrowing funds to maintain your position, and just like any loan, interest applies.
For example, when trading CFDs (Contracts for Difference), you're borrowing money from the broker to control a larger position, which incurs interest. Think of it as a small financing cost or income for "renting" your trading position overnight.
In forex trading, swap charges stem from the interest rate differential between the two currencies in a pair. Each currency has an interest rate set by its central bank, and when you hold one currency against another, you must account for those rates. If you buy a currency with a higher interest rate against a currency with a lower rate, you earn the interest difference (a positive swap). Conversely, if you are long the lower-yielding currency and short the higher-yielding one, you pay the difference (a negative swap). For that matter, many investors are looking for currency pairs that may provide them with a fixed income over a period of time.
To know the swap rate incurred on each currency, you can visit our swap rates page before entering a position. Here's what it looks like:
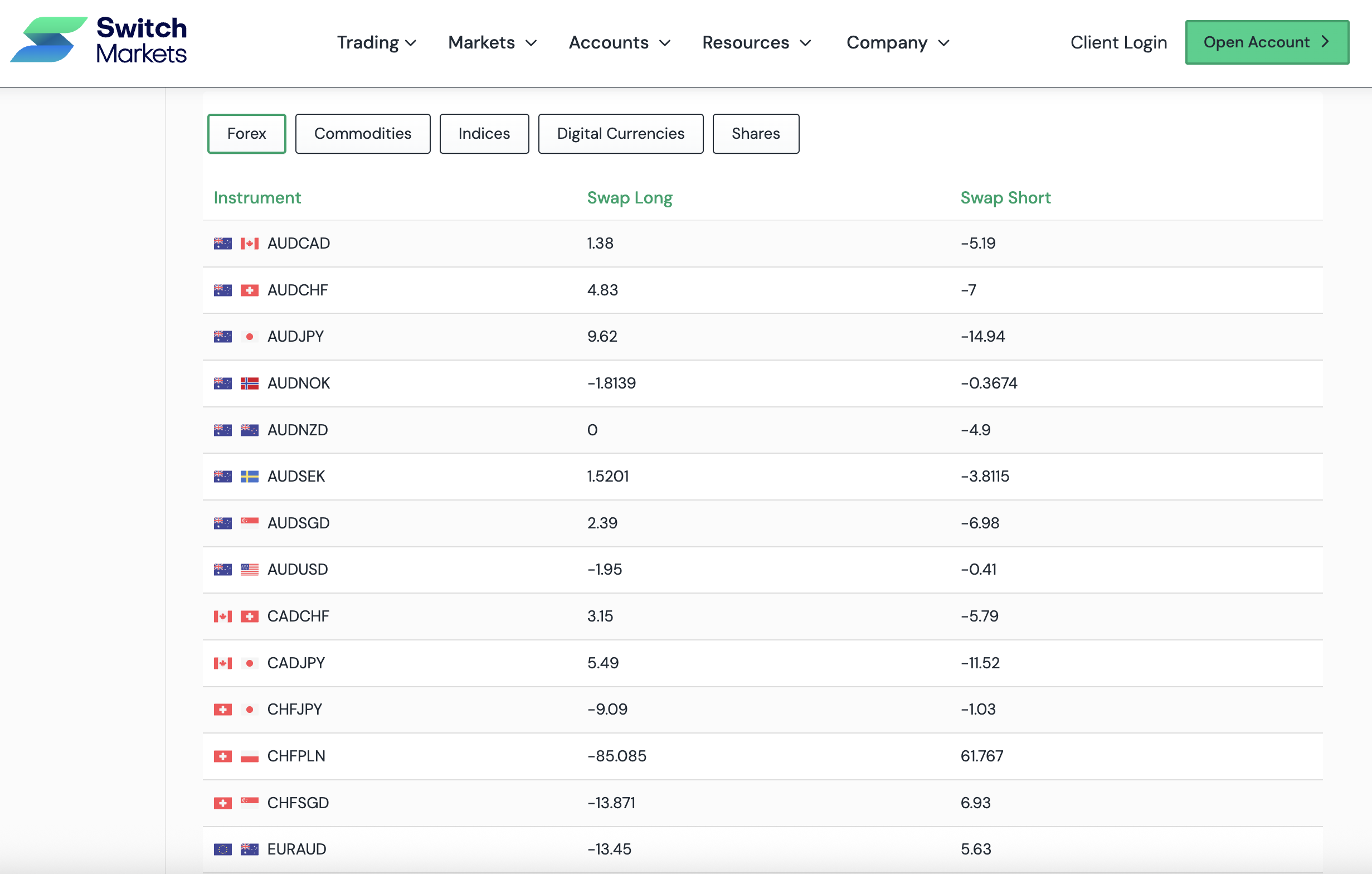
As you can see in the image above, Switch Markets gives you the swap rates for each position you plan to take - a long or short position.
Keep in mind that brokers typically handle this automatically: at the end of each trading day (often at a specified "cut-off" time, like 5 pm New York time in forex), they apply the appropriate swap rate to your open positions. The adjustment shows up in your account as either a debit (fee) or a credit, reflecting the cost or yield from holding that position overnight.
In CFD trading on other instruments (indices, stocks, commodities), swap rates follow the same principle of overnight financing. If you hold a CFD past the daily cut-off, an interest adjustment is made to your account to cover the cost of funding the leveraged portion of your position. For instance, if you hold a stock index CFD overnight, you're charged an interest fee because the broker has financed the bulk of that trade (minus your margin).
Many brokers add a small admin markup (for example, +2% or +3% above the benchmark interest rate) as part of the swap rate. The core idea is that any time you use leverage and hold past the trading session, there will be an interest impact, either a cost to you or, in some cases, interest payments to you.
It's worth noting that swap rates in trading are distinct from interest rate swaps (the latter being a type of derivative contract used in financial institutions). Here, we're focusing on the overnight rollover rates relevant to retail trading in forex and CFDs. Swap rates are also sometimes called overnight fees or rollover fees, but all these terms refer to the same concept of interest adjustments on held positions.
In forex and CFD trading, swap rates are the overnight financing charges or credits applied to long and short positions held beyond the trading day's close. In simpler terms, they are the interest paid or received on a trade carried into the next day. These rates exist because when you trade on margin, you are effectively borrowing funds to maintain your position, and just like any loan, interest applies.
Swap Rate Example
To understand how forex swap rates affect a trade, let's walk through a simple example. Imagine you're trading the EUR/USD currency pair. Suppose the Eurozone interest rate is slightly higher than the U.S. interest rate, resulting in an interest rate differential of about 1.5% in favor of the euro.
Now, say you buy 1 standard lot of EUR/USD (which is 100,000 units of EUR). If you hold this long position overnight, you are long the higher-interest account currency (EUR) and short the lower-interest currency (USD). In this scenario, you would earn a positive swap because of the 1.5% fixed rate difference. How much exactly?
Using a typical swap calculation, the daily interest is determined by the position size, interest rate differentials, and the time period. For a 100,000 EUR/USD position with a 1.5% annual rate difference, the overnight interest comes out to roughly:
Overnight Interest = 100,000 × (0.015 / 365) ≈ 4.11 (in the quote currency, USD)
This means you would earn about $4.11 per day in that position as swap income. If you held the position for 30 days, in theory, you'd accumulate around $123 in positive interest, assuming the exchange rate and position size remain the same and ignoring any broker fees or changes.
Now, if the situation were reversed and you shorted 1 lot of EUR/USD under the same conditions, you'd short the higher-rate currency and long the lower-rate one. In that case, the 1.5% difference works against you, and you'd be charged roughly $4.11 per day to hold the position. Over a month, that could mean about $123 deducted from your account in swap fees.
This example illustrates two important points: swap rates can be either a small bonus or a small penalty on your trades each day, and over time, those small amounts add up. Also, notice that the swap is proportional to the trade size – a larger position yields a larger interest cost or credit.
Most brokers publish a schedule of swap rates (often expressed in pips or dollar terms per lot) for each instrument, so you can check the exact amount you'll pay or receive per day for a given trade. It's wise to familiarize yourself with these rates for the assets you trade, especially if you plan to hold positions for more than a day.
How May Swap Rates Impact Your P&L?
Swap rates might seem trivial at first, just a few dollars per day on a standard lot in the example above, but they can significantly impact your profit and loss over time. The effect largely depends on your trading style and the duration of your trades.
For short-term traders, swap rates are a non-factor; if you never hold a trade overnight, you never incur a swap at all. In this case, you can ignore swaps entirely in your P&L calculations, since they won't appear.
However, for swing traders and long-term investors who hold positions for days, weeks, or even months, those daily interest adjustments become very real. A few dollars a day can turn into tens or hundreds of dollars over a long holding period. This can erode your profits or increase your losses. In fact, cumulative swap costs can undermine gains from the trade itself if they are not accounted for.
For example, you might be up 100 pips on a position, but if you paid 5 pips worth of swap every day for 30 days, that's 150 pips in fees, enough to completely offset your profit. This is why savvy traders pay attention to swap rates: they are part of the true cost of a trade.
One tricky aspect of swap charges is that they often go unnoticed. Unlike a one-time commission or a wide bid-ask spread that you see immediately, swaps trickle out slowly. As one trading author aptly noted, the danger of swap fees is "how invisible they feel until it’s too late". You might not notice the impact on any single day, but over time, you might wonder why your account balance is lower than expected. The silent drip of overnight fees could be the culprit. Some have even called swap fees “the silent killer” of traders' accounts for this reason.
On the flip side, swaps can also have a positive impact on your P&L if you are earning interest, although this can only be applied in the Forex market. A well-known strategy called the carry trade involves holding positions where you collect more interest than you pay. In a profitable carry trade, the swap credits act like a steady tailwind, adding to your P&L. While price action still determines most of the outcome, a positive swap can boost your overall returns or cushion some downside. However, positive swaps are not a guarantee of an overall profitable trade but just an extra factor in your favor. You still need the market to cooperate, and you need to be mindful that brokers can change swap rates (they typically adjust them based on interbank rates and their own policies). In addition, you also need to be aware of CFD rollovers, which is a scenario in which the brokers shift contracts.
Either way, swaps must be monitored regularly, which is easy to do on advanced platforms like MetaTrader 4 and 5. As you see in the image below, on MT4/5, you can find the swap fees for every trade in the Trade Summary window.

In summary, swap rates directly affect your net profitability on trades held overnight. For brief trades, the effect is negligible; for prolonged trades, it can become substantial. As a trader, you should monitor swap costs just as you would spreads, commissions, or any other trading cost. They are the carrying cost of your positions and are therefore an integral part of your trading performance.
The danger of swap fees is "how invisible they feel until it’s too late". You might not notice the impact on any single day, but over time, you might wonder why your account balance is lower than expected.
How to Use Swap Rates in Your Trading Strategy
Successful traders account for every cost and opportunity, and swap rates are no exception. Here are some ways you can use or manage swap rates in your trading strategy:
Leverage Positive Swaps (Carry Trading)
If you plan on holding a position long-term, consider the interest rate differential as part of your trade selection. By going long on a currency (or asset) with a higher interest rate and short on one with a lower rate, you earn a positive swap each day. This is the essence of the carry trade strategy: you not only aim for profit from price movement but also collect daily interest income. Over weeks or months, this extra income can be significant.
For example, a trader might favor buying a currency like AUD (if Australian rates are high) against JPY (if Japanese rates are low) to pocket the interest difference daily.
Pro tip: Always verify the current swap rates with your broker; economic conditions change, and a pair that yielded positive swap last year might not do so this year if interest rates shift.
Minimize Negative Swap Costs
When holding positions with a negative swap, be strategic to reduce the bite. One approach is to limit the holding period. If you only need to stay in a trade for a few days, the swap cost might be negligible, but if it looks like you'll need to hold for months and the swap is heavily against you, reassess the trade. Ensure that your expected profit justifies the accumulated fees.
In some cases, you might choose an alternative instrument to express the same market view. For instance, instead of holding a cash index CFD with a high overnight fee, you could trade an index futures contract, which has no daily financing charge (the carry cost is built into the futures price).
Likewise, in forex, if one side of the pair has a drastically higher interest rate, you might prefer to wait for a better entry or use options/futures to avoid daily costs. Another tactic is to close positions just before the rollover time and reopen them afterwards, although this can incur extra spread/commission costs. This method is only viable if those costs are less than the swap you'd pay (and requires careful timing).
Choose the Right Account Type or Broker
If swap rates are a major concern (for example, you plan to hold long-term positions frequently or you follow religious principles that prohibit earning/paying interest), look into a swap-free account option, also known as an Islamic trading account.
Some brokers, including Swiitch Markets, offer swap-free (Islamic) trading accounts where no overnight interest is charged or credited. These accounts sometimes replace the swap with a fixed fee or require certain conditions, but they can be useful for avoiding interest altogether. Make sure you understand any alternate fees the broker might charge in place of swaps.
Additionally, brokers can differ significantly in their swap rate offerings, so doing a bit of homework to compare swap rates may lead you to a broker that offers more favorable terms for the instruments you trade.
Incorporate Swap into Risk Management
Treat swap costs like any other cost in trading. Before you enter a position, especially a large one you expect to hold, calculate what the swap could total if you keep the trade open for your intended duration.
For example, if you're entering a trade that might run for 30 days and you know the swap is –$5 per day, realize that about –$150 will be added to your loss or subtracted from your profit in that time. This might affect your decision on position sizing or whether to take the trade at all. By anticipating the swap impact, you avoid surprises. Some trading platforms even display the current daily swap rates and can show you the accumulated swap on your open positions.
Use this information to adjust your strategy: you might take partial profits sooner on a negatively swap-bearing trade, or conversely, be more patient with a positively swapped trade since it's paying you to stay in.
Final Word
To sum up, swap rates might not be the flashiest aspect of trading, but they play a crucial role in long-term trading success. Understanding what swap rates are and how they affect your P&L is part of becoming a well-rounded trader. It's about seeing the big picture: profit and loss are not only decided by entry and exit prices, but also by what happens in between — including overnight holding costs or gains.
By now, you should appreciate that every overnight position accrues an interest effect. This knowledge allows you to plan your trades better. You can avoid unpleasant surprises by factoring swaps into your expected returns, and you can even design strategies to benefit from favorable swaps. Whether you choose to seek positive swap opportunities or simply avoid large negative swap drags on your account, the key is to be aware and proactive.
In trading, edges often come from the cumulative effect of many small factors. Swap rates are one such factor. A trader who ignores them might give up a portion of their edge without realizing it, whereas a trader who manages them wisely gains an extra advantage (or at least removes a potential handicap).
So the final word is this: treat swap rates with the respect they deserve. Check what you're being charged or paid each night, stay informed about interest rate trends (since these drive swaps), and align your trading tactics accordingly. This way, you'll ensure that overnight financing works for you, not against you, as you pursue trading success.
FAQs
Here are quick answers to two common questions traders often ask about swap rates.
How do swap rates work in trading?
Swap rates are the interest you earn or pay for holding a position overnight, based on the interest rate difference between the currencies (or asset financing costs). Positive swaps add to your profit, negative swaps reduce it—making them an important factor in long-term trades.
How can you avoid swap fees in forex and CFD trading?
Close your trades before the daily rollover time, use swap-free (Islamic) accounts, or trade instruments like futures that don’t charge overnight interest.
Can swap rates work to your benefit?
Yes. If you're long on the higher-interest asset and short on the lower one, you can earn daily interest (a positive swap), especially in carry trade setups.
Risk Disclosure: The information provided in this article is not intended to give financial advice, recommend investments, guarantee profits, or shield you from losses. Our content is only for informational purposes and to help you understand the risks and complexity of these markets by providing objective analysis. Before trading, carefully consider your experience, financial goals, and risk tolerance. Trading involves significant potential for financial loss and isn't suitable for everyone.
